Your Brain consumes more energy, more water, and more oxygen than other organs in your body. Now think about which consumes more things which means it performs more than any other organ.
There is no doubt that your brain is the most important part of your body. It manages almost all the functions of your body. But you know one interesting fact about your brain your brain is a chemical factory. Your brain can produce almost all the chemicals that you find in a pharma shop.
The chemicals in the brain are produced by your thoughts. This means all the chemicals are thought-dependent.
List of Brain Chemicals
There are numerous brain chemicals, or neurotransmitters, that play important roles in the brain’s functioning. Here is a more comprehensive list of brain chemicals along with their primary functions:
1. Dopamine: Regulates reward and pleasure, motivation, movement, attention, and learning.
2. Serotonin: Involved in mood regulation, sleep, appetite, digestion, and social behavior.
3. Norepinephrine (noradrenaline): Contributes to arousal, alertness, attention, and the “fight-or-flight” response.
4. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid): Inhibits neuronal activity, promoting relaxation, reducing anxiety, and controlling muscle tone.
5. Glutamate: Acts as the primary excitatory neurotransmitter, involved in learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity.
6. Acetylcholine: Important for learning, memory, muscle movement, and the functioning of the peripheral and central nervous systems.
7. Endorphins: Natural painkillers and mood regulators, producing feelings of pleasure and euphoria.
8. Oxytocin: Plays a role in social bonding, trust, empathy, and maternal-infant attachment.
9. Histamine: Involved in wakefulness, attention, learning, and allergic responses.
10. Cortisol: Known as the “stress hormone,” it helps regulate the body’s response to stress and inflammation.
11. Melatonin: Regulates the sleep-wake cycle and is involved in maintaining circadian rhythms.
12. Anandamide: A cannabinoid neurotransmitter associated with mood, pleasure, and pain perception.
13. Adenosine: Contributes to sleep regulation, alertness, and the dilation of blood vessels.
14. Glycine: Inhibits neuronal activity in the spinal cord and brainstem, playing a role in motor control and pain perception.
15. Substance P: Involved in the transmission and perception of pain signals.
16. Neuropeptide Y: Regulates appetite, stress response, and cardiovascular function.
17. Vasopressin: Important for water balance, social behavior, and regulating blood pressure.
18. Cholecystokinin: Regulates appetite, digestion, and anxiety.
19. Epinephrine (adrenaline): Released during stressful situations, it increases heart rate, blood pressure, and energy availability.
20. Prostaglandins: Lipid compounds involved in various physiological processes, including inflammation and pain signaling.
This list represents a range of brain chemicals, each with its own unique functions and effects on the brain and body. It’s important to note that these chemicals often interact and influence one another, and their precise roles are still the subject of ongoing research.
4 Main Brain Chemicals
By understanding the role of these primary brain chemicals, you can have a better understanding of how they are affecting you in everyday situations. The more you know, the more you’ll be able to take control of the effects of brain chemicals. You can enjoy a healthier and happier life.
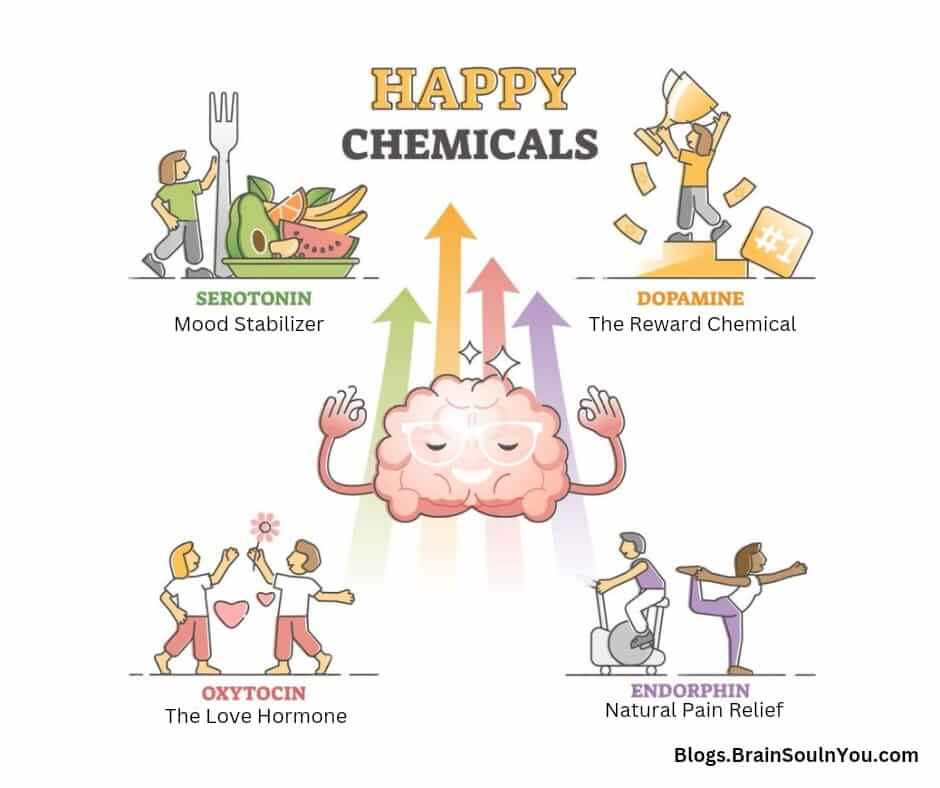
Four primary chemicals can drive the positive emotions you feel throughout the day: dopamine, oxytocin, serotonin, and endorphins (sometimes referred to as D.O.S.E.). Each of these chemicals plays a huge part in the way our bodies function: physically, mentally, and emotionally.

Dopamine: Chemical messenger
Dopamine is a type of neurotransmitter. Your body makes it, and your nervous system uses it to send messages between nerve cells. That’s why it’s sometimes called a chemical messenger.
Dopamine is a pretty dope chemical as it plays a role in “how you feel pleasure”. It helps you to focus when learning or working. This brain chemical enables you to find things interesting. It plays a pretty significant part in thinking, planning, motivation, sleep, mood, and attention.
Consumption of Alcohol and Drugs such as cocaine produces dopamine and makes the consumer feel happy, excited, and high. But, it is not recommended to consume alcohol and drugs as they have negative long-term effects, such as addiction, and heart attacks and they can surface mental health problems.
Research also proves that using mobile phones, gambling, playing video or mobile games, and smoking also produces dopamine because while consuming these a person gets pleasure. That’s the reason a person becomes addicted to the things that give them pleasure.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays an important role in various brain functions. Here are some key aspects of dopamine:
Key Aspects of Dopamine
Reward and Pleasure: Dopamine is closely linked to the brain’s reward system. It is released when we experience something pleasurable or beneficial, such as eating delicious food, engaging in enjoyable activities, or receiving positive social interactions. It reinforces behavior by creating a sense of pleasure and motivates us to seek those rewarding experiences again.
Motivation and Drive: Dopamine is involved in motivation, goal-directed behavior, and the drive to pursue rewards. It helps us initiate and sustain activities required to achieve desired outcomes. When dopamine levels are disrupted, it can lead to decreased motivation and difficulty experiencing pleasure, which are symptoms seen in conditions like depression.
Movement and Motor Control: Dopamine is essential for coordinating movement and motor control. It is produced in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain involved in the regulation of movement. Insufficient dopamine production in this area is linked to movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease, which is characterized by tremors, rigidity, and difficulty with voluntary movements.

Attention and Focus: Dopamine plays a role in attention and focus. Optimal dopamine levels are important for maintaining alertness, maintaining attention to tasks, and filtering out irrelevant information. ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) is associated with dysregulated regulation of dopamine, resulting in difficulty with attention and impulsivity.
Learning and Memory: Dopamine is involved in the process of learning and forming memories. It helps strengthen neural connections and facilitates the encoding of information into long-term memory. Changes in dopamine signaling can impact learning abilities and memory formation.
Mood Regulation: Dopamine is implicated in mood regulation, although its role is complex and not fully understood. Imbalances in dopamine levels have been associated with various mood disorders, including depression and bipolar disorder.
It is important to note that dopamine’s effects are not solely positive or negative. Its role depends on the specific brain regions involved, the receptors it interacts with, and the overall balance of neurotransmitters in the brain. Dysfunction or dysregulation of dopamine signaling can contribute to a range of neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Oxytocin: Love Chemical in Brain
You may not have heard of oxytocin, but you’ll have felt the effects of this brain chemical at least once in your lifetime. Oxytocin is the chemical that is referred to as a “Love Chemical” also. Because levels of oxytocin increase during hugging and orgasm. It makes you social and helps in building relationships with trust and loving feelings.
The release of oxytocin is known to create a warm and fuzzy feeling. It plays an important role in sexual activities and orgasms. It is heavily present in couples in the first stages of their relationship. It plays an important part in trust, empathy, positive communication, and the processing of bonding cues.

Oxytocin is a hormone and neurotransmitter often referred to as the “love hormone” or “cuddle hormone.” It plays a significant role in social bonding, trust, empathy, and various physiological processes. Here are some key aspects of oxytocin:
Key Aspects of Oxytocin
Social Bonding: Oxytocin is released during social interactions, particularly those involving positive social bonds. It promotes feelings of attachment, closeness, and bonding between individuals. Oxytocin is released during activities like hugging, cuddling, breastfeeding, and intimate interactions, strengthening emotional connections.
Trust and Empathy: Oxytocin is associated with the development of trust and promotes prosocial behaviors. It enhances empathy and the ability to understand and share the emotions of others. Oxytocin can influence how we perceive and respond to social cues, facilitating social cooperation and altruistic behavior.
Childbirth and Breastfeeding: Oxytocin plays a crucial role during childbirth and breastfeeding. It triggers uterine contractions during labor and stimulates milk let-down during breastfeeding. Oxytocin helps facilitate the mother-infant bond and promotes nurturing behaviors.
Stress Regulation: Oxytocin has stress-reducing effects. It can help lower cortisol levels, which is the hormone associated with stress. Oxytocin promotes relaxation, reduces anxiety, and contributes to a sense of well-being.
Sexual Function: Oxytocin is involved in sexual arousal and orgasm. It is released during sexual activity and promotes feelings of pleasure and intimacy. Oxytocin can contribute to the emotional bond between sexual partners.
Parental Behavior: Oxytocin plays a role in parental behavior, both in mothers and fathers. It fosters nurturing behaviors and promotes parental attachment and caregiving.
It’s important to note that the effects of oxytocin can vary depending on the context and individual differences. While oxytocin is often associated with positive social behaviors, it can also influence negative emotions, such as jealousy and aggression, in certain circumstances. Oxytocin’s role in human behavior and its potential therapeutic applications are still areas of ongoing research and exploration.
Serotonin: Happy Chemical in Brain
It is sometimes known as the “happy chemical” because it provides feelings of happiness, positivity, and well-being. Several studies have been conducted over the years which suggest serotonin increase can help to treat and prevent symptoms of depression.
It is believed that levels of serotonin can be increased through exercise, a balanced diet, and introducing more bright natural lighting. It helps in sleep, arousal, sexual desire, emotions, digestion, and cognitive and autonomic functions. Serotonin also affects bone growth and even organ development.
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in various physiological and psychological functions. Here are some key aspects of serotonin:
Key Aspects of Serotonin
Mood Regulation: Serotonin is often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter because it contributes to feelings of well-being and happiness. It helps regulate mood and emotions, promoting a sense of contentment and stability. Low levels of serotonin have been linked to conditions like depression, while certain medications that increase serotonin levels, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are used in the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders.
Sleep and Circadian Rhythms: Serotonin is involved in the regulation of sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythms. It helps promote sleep and regulates the timing and quality of sleep. Imbalances in serotonin levels can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to sleep disorders.
Appetite and Digestion: Serotonin plays a role in regulating appetite, satiety, and food intake. It helps control cravings and can contribute to a feeling of fullness after a meal. Serotonin is also involved in digestive processes, including the contraction of smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract.

Cognition and Memory: Serotonin is involved in cognitive functions such as learning, memory, and attention. It helps modulate cognitive processes and influences information processing, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities.
Pain Perception: Serotonin is involved in the modulation of pain signals. It can both enhance and inhibit pain perception, depending on the specific receptors and brain regions involved.
Social Behavior: Serotonin is implicated in social behavior and social interactions. It contributes to social cognition, empathy, and prosocial behavior. Altered serotonin levels have been associated with certain psychiatric conditions characterized by social difficulties, such as autism spectrum disorders.
It’s important to note that serotonin interacts with other neurotransmitters and is influenced by various genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Imbalances in serotonin levels or disruptions in serotonin signaling have been linked to several neurological and psychiatric disorders. However, the understanding of serotonin’s complexities and its exact role in various conditions is an ongoing area of research.
Endorphins: The Natural Painkiller
Endorphins are essentially released in response to pain. It helps you to push your body beyond your comfort level. That’s why it is also referred to as The Natural Painkiller. It is released when you are injured, experience stress, eat, after 30 minutes of exercise, or have sex.
When endorphins are released they can help to relieve pain, reduce stress, and may cause a euphoric feeling. In short, they can make you feel pretty darn good.
Endorphins are natural chemicals produced by the body that function as neurotransmitters and have pain-relieving and mood-enhancing effects. Here are some key aspects of endorphins:
Key Aspects of Endorphins
Pain Relief: Endorphins act as natural painkillers. They bind to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, reducing the perception of pain and promoting a sense of well-being. Endorphins are released in response to various stimuli, including physical exercise, stress, laughter, and certain activities that induce pleasure.
Mood Enhancement: Endorphins contribute to feelings of euphoria, pleasure, and general well-being. They can improve mood and provide a sense of happiness and contentment. Endorphin release is associated with activities like exercise, certain types of social interactions, and engaging in enjoyable hobbies.
Stress Reduction: Endorphins play a role in stress reduction and can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on the body and mind. They can promote relaxation and contribute to a calmer state of mind.
Exercise and Runner’s High: Physical exercise, particularly aerobic activities, can trigger the release of endorphins. This is often associated with the phenomenon known as “runner’s high,” a feeling of euphoria and well-being that occurs during or after intense exercise.
Regulation of Appetite and Food Cravings: Endorphins may influence appetite regulation and food cravings. They can contribute to feelings of satisfaction and fullness after a meal, potentially reducing the desire for further food consumption.
Modulation of Immune Function: Endorphins can modulate immune system activity. They may influence the body’s inflammatory response and contribute to the regulation of immune functions.
It’s important to note that endorphins are just one of several neurotransmitters involved in pain modulation and mood regulation. Other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin, also contribute to the complex interplay of emotions, pain perception, and well-being. The release and effects of endorphins can vary among individuals and different situations, and the exact mechanisms underlying their functions are still being explored by researchers.
Placebo Effect
There is a term Placebo effect in psychology. The placebo effect basically works the chemical in the brain. If a person expects a pill to do something, then it’s possible that your brain chemistry can cause effects similar to what a medication might have caused.

One research on the placebo effect has focused on the relationship between mind and body. One of the most common theories is that the placebo effect is due to a person’s expectations. If you take any vaccine or medicine by faith, it affects you more and gives you positive results.
Some other Interesting Facts about Brain Chemicals
According to science brain can produce any chemical as it thinks. Suppose, somebody, talks about any sour thing like lemon, and you suddenly start feeling the sour taste in your mouth. When you see some delicious food your mouth fills with water and you start craving that food.
The research was done to prove that your brain can produce all chemicals. Some scientists visited a jail. There a thief was to be killed by an electric shock. They told the jailer there that we will kill it with a poisonous snake. This thing was also given in the mind of that thief. He kept thinking about the poisonous snake all night now.
In the morning, when he was to be bitten by a snake, his mouth was covered with a black cloth, and two pins were chewed on him as if a snake had bitten him. In no time he went blue and died. When those scientists examined his blood, snake venom was found in it.
Most of the diseases in your body are because of negative thinking that produces negative chemicals and causes the diseases. Diabetes, Blood Pressure, asthma, cancer, arthritis, etc are some examples of diseases caused by negative thoughts and emotions. You can heal from these diseases by changing your thoughts and mindset.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q: What are the main brain chemicals and their functions?
- A: The main brain chemicals, or neurotransmitters, include dopamine, serotonin, oxytocin, and endorphins. They play crucial roles in regulating mood, pleasure, motivation, social bonding, and pain relief.
- Q: How does dopamine affect the brain and body?
- A: Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that regulates reward, pleasure, motivation, movement, attention, and learning. It plays a role in mood, focus, and the brain’s reward system, and its levels can be influenced by various activities, including exercise and certain substances.
- Q: What is oxytocin, and how does it contribute to love and bonding?
- A: Oxytocin, often referred to as the “love hormone,” plays a key role in social bonding, trust, empathy, and maternal-infant attachment. It is released during activities like hugging, cuddling, and orgasm, promoting positive social connections.
- Q: Can serotonin influence mood and how is it related to depression?
- A: Serotonin, known as the “happy chemical,” regulates mood and emotions. Imbalances in serotonin levels have been linked to conditions like depression. Medications like SSRIs, which increase serotonin levels, are used in the treatment of depression and anxiety.
- Q: What is the placebo effect, and how does it impact brain chemistry?
- A: The placebo effect is a phenomenon where the expectation of a treatment produces therapeutic effects, even if the treatment has no active ingredients. It demonstrates the powerful connection between the mind and body, influencing brain chemistry and producing physiological responses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q: Can thoughts really influence the production of brain chemicals?
- A: Yes, thoughts have a profound impact on the production of brain chemicals. Positive thoughts can stimulate the release of chemicals like dopamine, serotonin, and endorphins, while negative thoughts may lead to the production of stress-related chemicals.
- Q: What is the significance of dopamine in the brain?
- A: Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in reward, pleasure, motivation, movement, attention, and learning. It influences mood, focus, and even motor control. The release of dopamine is associated with feelings of pleasure and reinforcement of behavior.
- Q: How does oxytocin contribute to social bonding and relationships?
- A: Oxytocin, often referred to as the “love hormone,” plays a key role in social bonding, trust, and empathy. It is released during activities like hugging, cuddling, and intimate interactions, fostering emotional connections and positive communication in relationships.
- Q: Can serotonin levels affect mood and well-being?
- A: Absolutely. Serotonin is known as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter and contributes to feelings of happiness and well-being. Imbalances in serotonin levels have been linked to mood disorders, and activities like exercise and a balanced diet can help regulate serotonin production.
- Q: How do endorphins act as natural painkillers?
- A: Endorphins, released in response to pain or stress, act as natural painkillers by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord. They reduce the perception of pain and promote feelings of pleasure and euphoria, contributing to pain relief and stress reduction.
Love,
Saurabh Goel
Read more blogs on “Hope Molecules” – The Secret to Mental Health!, Split Brain Theory
Saurabh Goel
He is the Founder and CEO of the Training and Counselling Company ‘Brain Soul & You’. He is an NLP Wellness Coach, Life Coach, Brain analyst, and Trainer for Education, Corporate, and Entrepreneurship. For more than 7 years, he delivered presentations on entrepreneurship, mind programming, and motivation. He did his B.tech in IT and later choose to be a successful psychologist. He is helping people in various ways through his counseling and training sessions.